The LibreZoom Podcast has collected some collaboration tools:
Category: Applications
[Nextcloud] Moving my NC installation
About two years ago I installed Nextcloud via the NextcloudPi script in an LXC Debian Stretch Container on my Proxmox Host. Since last year there is a new Debian release called Buster and I wanted to upgrade my container. But somehow it was not possible… there was something broken and on every upgrade I tried, a swap error came up. I searched for hours, but couldn’t find any solutions to this error, so I had to move my whole Nextcloud installation to a new debian buster container. I took the chance to create the new container as unprivileged container. Since I had no experience moving a complete Nextcloud instance, I first read the NC Wiki and had a look at some tutorials. Finally I followed C. Riegers awesome guide on backing and restoring a Nextcloud instance.
Everything went well until step 9.
root@nc:/var/www/nextcloud# sudo -u www-data php /var/www/nextcloud/occ maintenance:data-fingerprint
An unhandled exception has been thrown:
Doctrine\DBAL\DBALException: Failed to connect to the database: An exception occurred in driver: SQLSTATE[HY000] [1698] Access denied for user 'ncadmin'@'localhost' in /var/www/nextcloud/lib/private/DB/Connection.php:64
As I’ve been restoring on a brand new LXC Buster container, of course a few things were missing. I restored my nextcloud database, but I also had to recreate the “ncadmin” dbuser and grant the right permissions. I looked up the ncadmin password in my nextcloud config.php and added the user.
mysql -u root -p
CREATE USER 'ncadmin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES on nextcloud.* to ncadmin@localhost;
Next try with step 9.
root@nc:/var/www/nextcloud# sudo -u www-data php /var/www/nextcloud/occ maintenance:data-fingerprint
An unhandled exception has been thrown:
...nextcloud Redis server went away in /var/www/nextcloud/lib/private/Memcache/Redis.php:54
Still no success. Hiting google brought me to this link. C. Rieger was already there. 🙂
While checking /etc/redis/redis.conf I noticed that in my nextcloud config.php there was a different path for redis.sock.
redis.conf
unixsocket /var/run/redis/redis-server.sock
config.php
'host' => '/var/run/redis/redis.sock',
After changing the path I rebooted the container and again tried step 9. Now with success and my Nextcloud instance was back online. I only had to add the new hostname to the trusted domains and could login again. The only thing I couldn’t get to work was the NextcloudPi functionality. Since I was only using the nextcloudpi auto upgrade scripts, I could live without that. I disabled and deinstalled the app from the user interface.
[WordPress] SyntaxHighlighter Ampersand character
Recently I noticed that the character & is displayed in the SyntaxHighlighter like this: &
To fix this, simply add this snippet of the user kaggdesign to /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/syntaxhighlighter/syntaxhighlighter.php
/**
* Filter to fix issue with & in SyntaxHighlighter Evolved plugin.
*
* @param string $code Code to format.
* @param array $atts Attributes.
* @param string $tag Tag.
*
* @return string
*/
function kagg_syntaxhighlighter_precode( $code, $atts, $tag ) {
if ( 'code' === $tag ) {
$code = wp_specialchars_decode( $code );
}
return $code;
}
add_filter( 'syntaxhighlighter_precode', 'kagg_syntaxhighlighter_precode', 10, 3 );
This can be done directly from the webinterface. Just go to Plugins -> Plugin Editor -> select the Plugin SyntaxHighlighter Evolved -> add the snippet to the end
[Nextcloud] Run OnlyOffice Document Server in Docker
If you don’t already have it, you first have to install Docker. Then just get the docker-compose.yml for OnlyOffice
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ONLYOFFICE/Docker-DocumentServer/master/docker-compose.yml
and activate the JSON Web Token validation.
nano docker-compose.yml
- JWT_ENABLED=true
- JWT_SECRET=your_secret
- JWT_HEADER=Authorization
Now just run the container.
sudo docker-compose up -d
To use OnlyOffice with Nextcloud, your container needs to reachable via https, so you need to add a subdomain and SSL Certificate in your Nginx reverse proxy. Then just go to your Nextcloud installation and install the OnlyOffice Addon. There just enter the new domain to your OnlyOffice Docker Container and the JSON Web Token. Office files should now be editable in OnlyOffice.
[Nextcloud] Maintenance mode
# Change into your nextcloud directory
cd /var/www/nextcloud/
# Enable Nextcloud-Maintenance mode
sudo -u www-data php occ maintenance:mode --on
# Do something...
# Disable Nextcloud-Maintenance mode
sudo -u www-data php occ maintenance:mode --off
[Nextcloud] Run NextCloudPi Docker with external storage
Links
NextCloudPi (Docs)
NextCloudPi on DockerHub
Current installation process (Outdated installation process, but contains some usefull information)
Installation
If you want to use the external storage app to mount an NFS share in Nextcloud, there are two ways when using Docker. Mount the NFS share directly inside the Docker container. This would be easier when the container is already up and runing. Or mount the NFS share on the Host and pass the mountpoint as an argument when creating the Docker container: -v /mnt/nfs/:/mnt/nfs/
DOMAIN=your.domain.com
docker run -ti -d -p 4443:4443 -p 443:443 -p 80:80 -v ncdata:/data -v /mnt/nfs/:/mnt/nfs/ --name nextcloudpi ownyourbits/nextcloudpi $DOMAIN --restart=unless-stopped
Now wait until you see ‘Init done’ in the logs.
docker logs -f nextcloudpi
ncdata
If you ever need direct access to your storage, you can find out where your files are located with:
docker inspect nextcloudpi
Scroll up to “Mounts” and look for the path behind “Source”.
"Source": "/var/lib/docker/volumes/ncdata/_data"
Now you still have to navigate through a few folders. I finally found my files here:
ls /var/lib/docker/volumes/ncdata/_data/nextcloud/data/ncp/files/
Update to latest NCP version
docker exec -it nextcloudpi ncp-update
[Docker] Wallabag installation
https://www.wallabag.org
https://github.com/wallabag/docker
Just replace https://your_domain with your domain.
docker run -d --name wallabag --restart=always -v /opt/wallabag/data:/var/www/wallabag/data -v /opt/wallabag/images:/var/www/wallabag/web/assets/images -p 80:80 -e SYMFONY__ENV__DOMAIN_NAME=https://your_domain -e SYMFONY__ENV__FOSUSER_REGISTRATION=false wallabag/wallabag
Check with docker ps if the docker container is successfully up and running. Now just add a new subdomain with ssl in your nginx-proxy-manager.
Default login is wallabag:wallabag.
Their corresponding android app is also available on F-droid: https://f-droid.org/en/packages/fr.gaulupeau.apps.InThePoche/
[NGINX] Monitoring Nginx using Netdata
Recently I saw this tutorial about monitoring Nginx with Netdata and tried it by myself. I have running Netdata on my Proxmox Host and Nginx inside LXC. So I could skip step 1 and 2 of the tutorial. Since I’m using the super simple nginx-proxy-manager, which comes as docker deployment, it took me some minutes to figure out, how to enable the Nginx ‘stub_status‘ module (which is step 3 of the tutorial). Here’s what I did.
SSH into the LXC where the Nginx Docker is running. Look up the nginx container name (root_app_1) and open a shell in the running container.
docker ps
docker exec -it root_app_1 /bin/bash
Check if the ‘stub_module‘ is already enabled. The following command should return: with-https_stub_status_module
I got it from here.
nginx -V 2>&1 | grep -o with-https_stub_status_module
Next add a location to the nginx ‘server {}‘ block in the default config, to make it reachable via Netdata. The tutorial goes to ‘/etc/nginx/sites-available/default‘, another tutorial is editing ‘/etc/nginx/nginx.conf‘, but I found the default config in ‘/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf’.
nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
If nano is not installed (bash: nano: command not found), just install it. Get more information here or here.
apt update
apt install nano -y
Insert the new location in the server { listen 80; …..} block. In my case I have running Netdata on my Proxmox host, so i added localhost and my Proxmox ip.
location /nginx_status {
stub_status;
allow 192.168.178.100; #only allow requests from pve
allow 127.0.0.1; #only allow requests from localhost
deny all; #deny all other hosts
}
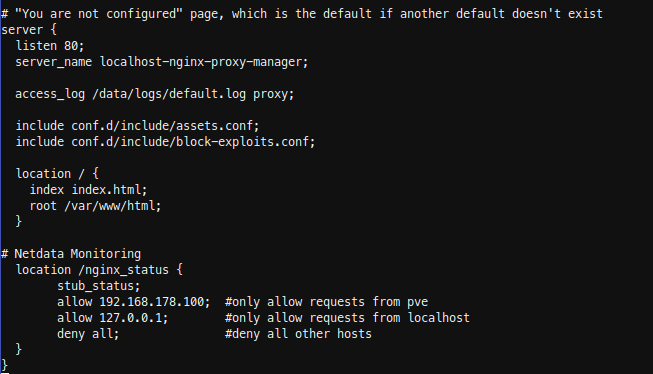
Save, exit your docker container and restart it.
docker restart root_app_1
SSH into Proxmox and check with curl, if you able to reach the new nginx location.
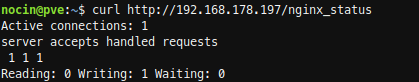
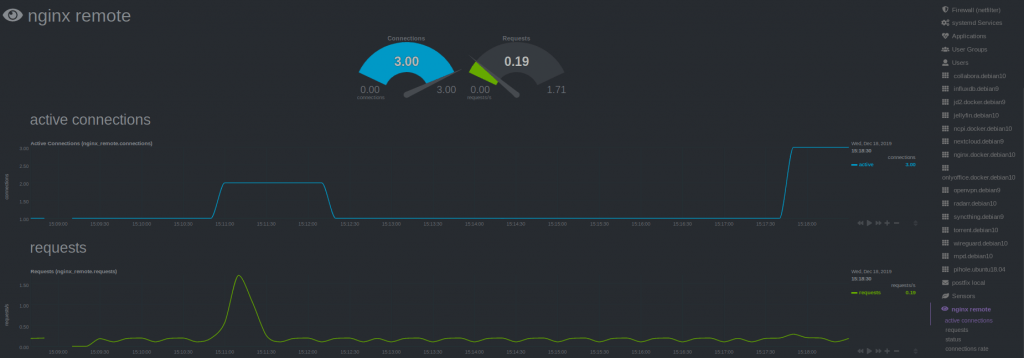
For the last step Configure Netdata to Monitor Nginx (step 4) , just follow the Netdata Wiki. Place a new file called nginx.conf on your Netdata host.
nano /etc/netdata/python.d/nginx.conf
Because Netdata is not running local, use ‘remote‘ following the url, instead of local and localhost.
update_every : 10
priority : 90100
remote:
url : 'https://192.168.178.197/nginx_status'
Restart Netdata and your are done.
sudo systemctl restart netdata
[Nextcloud] Installing Collaboraoffice in LXC
Both, Nextcloud and Collabora, are recommending the Docker installation for Collaboraoffice (here and here). But I wasn’t able to get the Collabora Docker Image running succesfully inside an Debian Buster LXC. There were appearing some errors and as far as I understand, it has something to do with running an LXC on ZFS. After spending about 3 hours I gave up and did a manual installation.
Installation
For a current installation guide, have look on their website here.
Install https support for apt and add Collabora CODE repository. (CODE = Collabora Online Development Edition)
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys 0C54D189F4BA284D
Add the Collabora CODE repository to the apt sources list.
nano /etc/apt/sources.list.d/collabora.list
Add the following line for Debian Buster:
deb https://www.collaboraoffice.com/repos/CollaboraOnline/CODE-debian10 ./
Now update the repository and install Collabora. (lool = LibreOffice OnLine)
sudo apt update
sudo apt install loolwsd code-brand
Configuration
You have to edit three sections in the config: SSL handling, inserting your Nextcloud domain as WOPI client and add some credentials for webinterface. So open the config with:
nano /etc/loolwsd/loolwsd.xml
- If you are using a reverse proxy (I have running a docker with nginx) which is managing all SSL certifactes, you don’t need local certifactes for your Collaboraoffice. So scroll down to the SSL settings, disable SSL and enable SSL termination.
<ssl desc="SSL settings">
<enable type="bool" desc="Controls whether SSL encryption is enable (do not disable for production deployment). If default is false, must first be compiled with SSL support to enable." default="true">false</enable>
<termination desc="Connection via proxy where loolwsd acts as working via https, but actually uses https." type="bool" default="true">true</termination>
- 2. Next add you Nextcloud domain in the WOPI storage section.
<storage desc="Backend storage">
<filesystem allow="false" />
<wopi desc="Allow/deny wopi storage. Mutually exclusive with webdav." allow="true">
<host desc="Regex pattern of hostname to allow or deny." allow="true">localhost</host>
<host desc="Regex pattern of hostname to allow or deny." allow="true">nextcloud\.domain\.org</host>
- 3. Add your credentials fot the webinterface.
<admin_console desc="Web admin console settings.">
<enable desc="Enable the admin console functionality" type="bool" default="true">true</enable>
<enable_pam desc="Enable admin user authentication with PAM" type="bool" default="false">false</enable_pam>
<username desc="The username of the admin console. Ignored if PAM is enabled.">user_name</username>
<password desc="The password of the admin console. Deprecated on most platforms. Instead, use PAM or loolconfig to set up a secure password.">super_secret_password</password>
Now restart loolwsd and check the status.
systemctl restart loolwsd.service
systemctl status loolwsd.service
Check if the https connection is working via browser https://ipaddress:9980 or curl:
curl -vkI https://localhost:9980
You can reach the webinterface with:
https://ipaddress:9980/loleaflet/dist/admin/admin.html
Reverse Proxy
Go to your reverse proxy, in my case it’s nginx proxy manager, and add another subdomain for collabora with an SSL certificate.
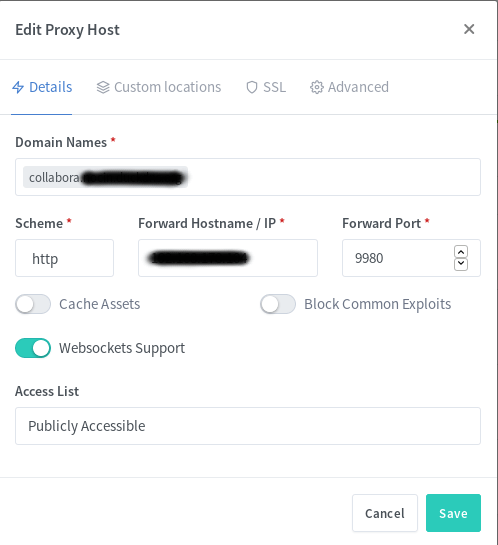
You also have to add a few custom locations. Look at the Collabora website for the some nginx configs. I used the second with “SSL terminates at the proxy”. I also added the given custom locations via the webui, e.g.:
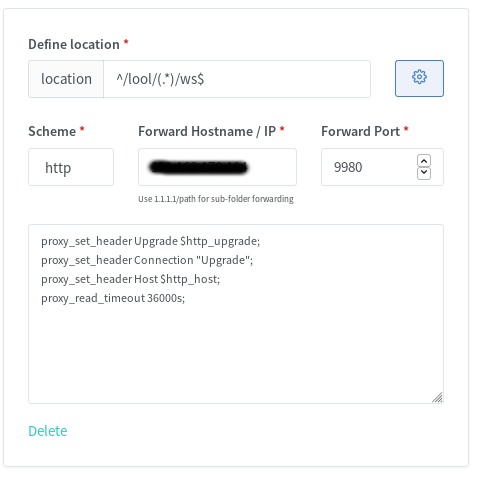
You should now be able to reach Collabora through your new subdomain via https.
https://collabora.your.domain.org/
And if you added /lool/adminws in your nginx config, you can also access the webui.
https://collabora.your.domain.org/loleaflet/dist/admin/admin.html
Install & configure Collabora Online App in Nextcloud
The easiest part is to install the Collabora Online App.
If done, go to Settings -> Collabora Online and set your Collabora Domain https://collabora.your.domain.org/ in here. Apply and edit your first excel in Nextcloud.
Done! 🙂
[NFS] Mount NFS Share inside VirtualBox VM
When receiving an error mounting an NFS share inside your VM:
sudo mount -t nfs xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:/data/media /mnt/nfs/media
mount.nfs: access denied by server while mounting xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:/mnt/nfs/media
Just change the network adapter of your VM in VirtualBox from “NAT” to “Bridge Mode”.
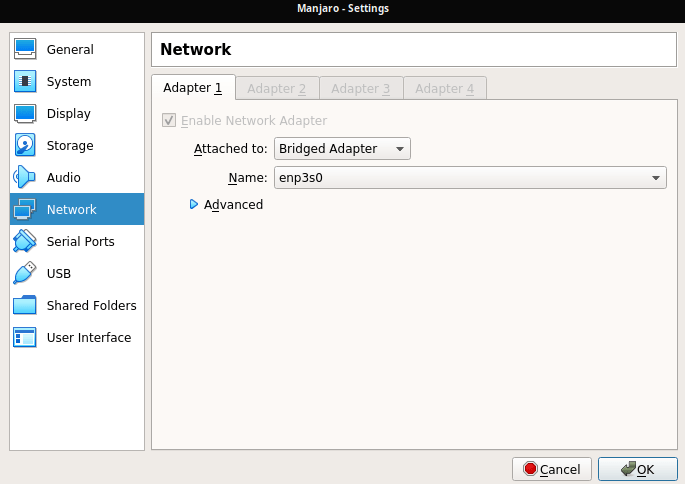
As alternative you can force the usage of the TCP protocol when mounting, like it is described here.
