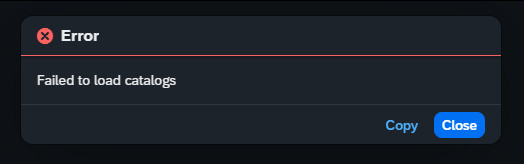
Recently, I was confronted with the “Failed to load catalogs” error message when starting the Fiori Launchpad (/ui2/flp) and navigating to the App Finder.
The system was quite new and the Fiori Customizing was not completely done yet. When opening the Dev Tools, I saw a failed request to
/sap/opu/odata/ui2/page_builder_pers/PageSets('%2FUI2%2FFiori2LaunchpadHome')
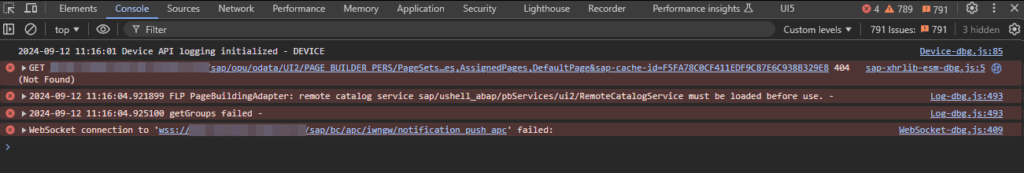
Opening this failed request in a new tab results in an HTTP 404 from an Apache web service. So it looked like an Apache was set up as reverse proxy in front of the sap system. I tried to call the PageSets endpoint without providing the key %2FUI2%2FFiori2LaunchpadHome and got an HTTP 200. So in general, Apache was working, and the service endpoint page_builder_pers was responding. Next, I did the same service calls from the gateway client and both calls were working fine. So it looked like Apache was the problem when providing the PageSets key. After a quick search, I found this post on Stack Overflow:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/37834925/apache-reverse-proxy-blocking-sap-fiori-launchpad-url
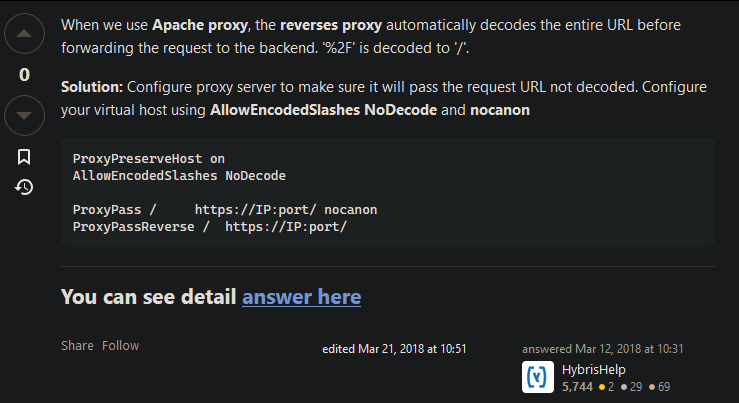
So the issue was some (in this case) incorrect decoding of ‘%2F’. After contacting the basis team and adding the proposed Apache configs, the request finally resolved successfully, and the Launchpad was displaying some apps.