https://github.com/Universal-Debloater-Alliance/universal-android-debloater-next-generation
[HR] Abwesenheiten (IT2001) – Anzeige Kontingentabtragungen
Bei einer Abwesenheit wie z.B. Urlaub, die über eine Monatsgrenze oder über einige Feiertage hinweg geht, kann es hilfreich sein, die konkreten Abtragungen einzusehen, um zu verstehen, welche Tage in dem Zeitraum denn wirklich Urlaub waren.
Dazu einfach die Abwesenheit öffnen in der PA20 und auf Springen → Abtragungen (Shift+F8) gehen.
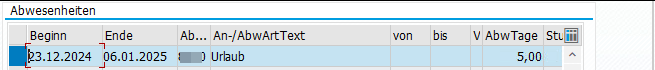
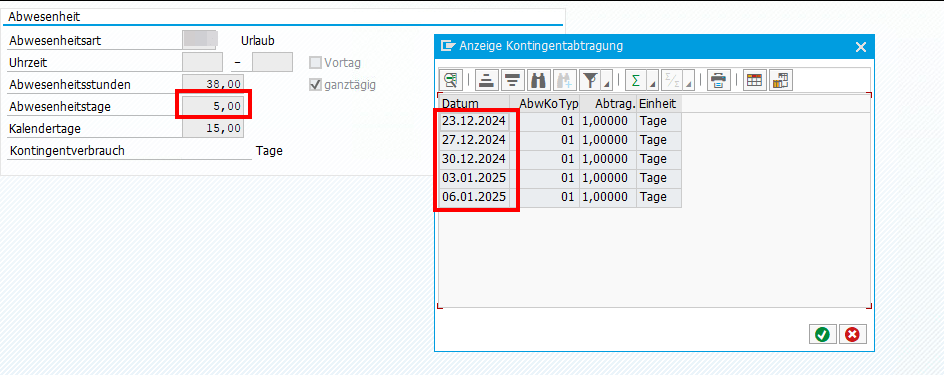
Man kann die Kontingentabtragung auch für das komplette Kontingent eines Jahres einsehen via IT2006.
Die zugehörige Datenbanktabelle ist PTQUODED. Um die Abträge für eine bestimmte Abwesenheitsart zu selektieren, muss noch ein JOIN auf die PA2001 über die DOCNR gemacht werden. Zumindest ist das der einzige Weg, den ich herausfinden konnte. 🙂
SELECT SUM( a~quode )
FROM ptquoded AS a
JOIN pa2001 AS b
ON a~pernr = b~pernr
AND a~docnr = b~docnr
INTO DATA(urlaubsabtrag)
WHERE a~pernr = pernr-pernr
AND a~datum BETWEEN pn-begda AND pn-endda
AND b~subty = 0100. " Abwesenheitsart, welche Selektiert werden soll
[Linux Mint] Preview files
Just noticed that you can preview files when selecting a file and pressing the space bar on the keyboard. It works for images, docs, audio, videos and even PDF files. You can simply close the preview using ESC. Really handy!
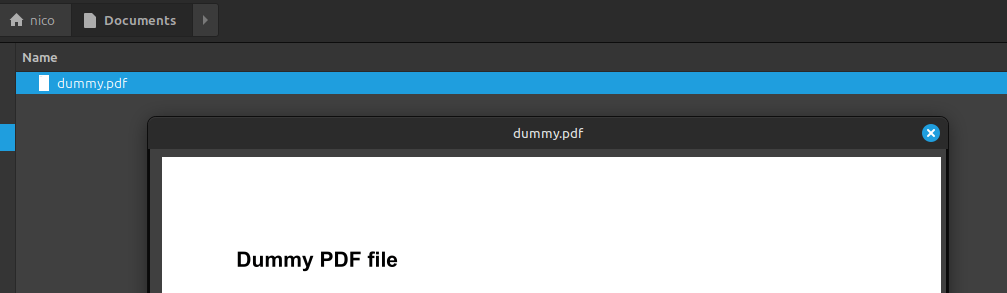
The responsible tool is called nemo-preview.
[DerpFest] Xiaomi Pad 5 (nabu)
I recently bought a used Xiaomi Pad 5 for 139.99€ from homezesting.com. It arrived in perfect condition.
The latest official Android version by Xiaomi is Android 13 with MIUI 14.0.5. This is kinda old, and I directly ran into an issue due to the old webview version in combination with the Home Assistant app (see here).
I therefore looked for a custom ROM and the first ROM I found for this device was DerpFest. I’ve never used it before, but flashing it shouldn’t be too different from other ROMs.
There are not much information on their website, but I found everything needed to know in their related telegram group: https://t.me/c/2284318430/8189
Unlocking the bootloader for Xiaomi devices can be annoying, but turned out, the bootloader of my purchased Pad 5 was already unlocked. Great!
(Update 10.02.2025: I asked the customer support and apparently they already sell all devices unlocked. Good to know!)
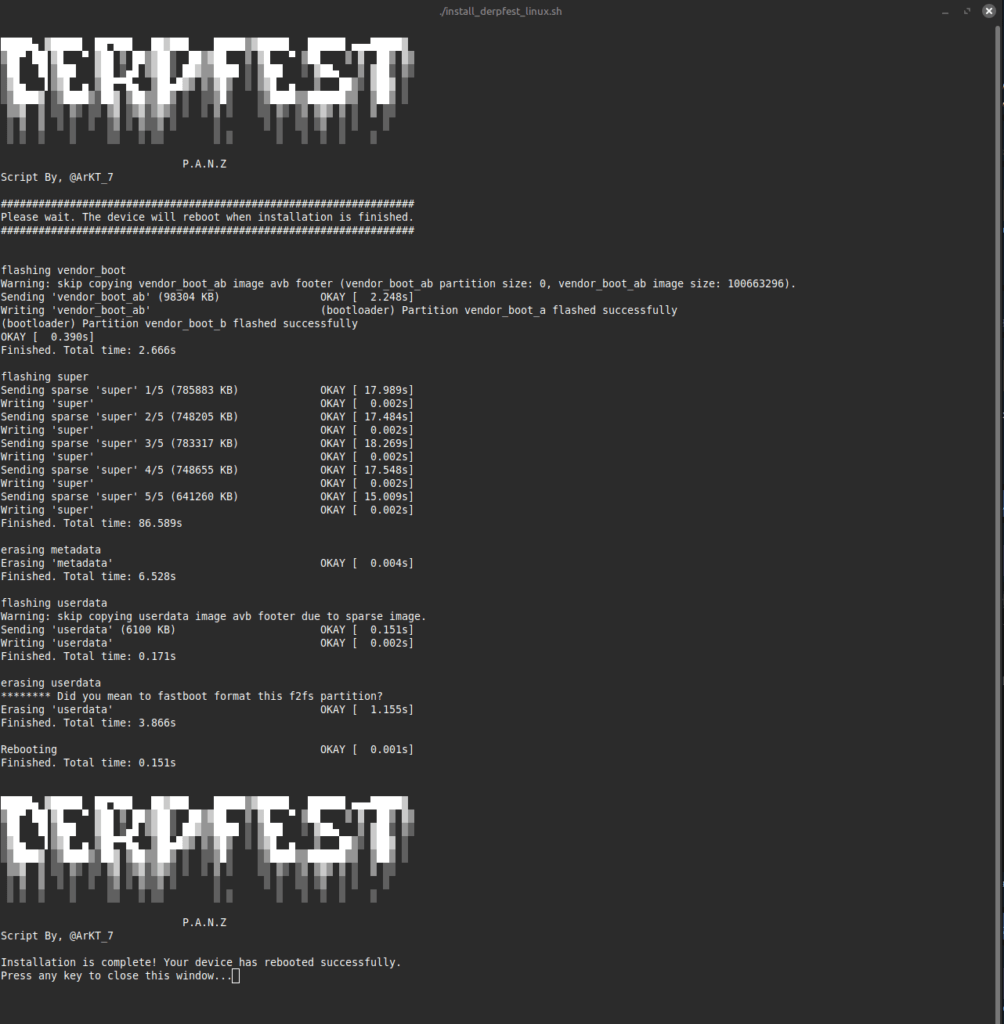
To make my life even simpler, I used the Auto-Installer shell script to install DerpFest 15. Unfortunately, it was running into an error, but it was easy to fix. (Seems like there is already a fixed version when downloading from GitHub here).
# make it executable
sudo chmod +x install_derpfest_linux.sh
# start script
./install_derpfest_linux.sh
# resulted in the error: /bin/bash^M: bad interpreter
# fix
sudo apt-get install dos2unix
dos2unix install_derpfest_linux.sh
./install_derpfest_linux.sh
Then the script ran without any issues.

When starting the device the first time, I skipped the Google Login step, so I wasn’t able to use the Play Store. But since not even a web browser is installed by default (which I think is really great to not be bloated from the beginning :-), I had to enable USB-Debugging mode and sideload F-Droid to install basic apps like a file explorer and browser.
adb install F-Droid.apk
The Tablet is running super smooth and so far I could not find any issues! 🙂
[Windows] “Super God Mode” For Windows
“This PowerShell script creates shortcuts to all special shell folders, named folders, task links, system settings, deep links, and URL protocols in Windows, providing easy access to a wide range of system settings and features.”
[ABAP] Get the last day of the previous month
I recently had to find the last day of the previous month. I found the Method get_last_day_prev_month of class cl_bs_period_toolset_basics doing the job. The actual logic is super simple:
rv_date = iv_date.
rv_date+6(2) = '01'.
rv_date = rv_date - 1.
That’s why I thought about whether I needed a separate method at all, or whether I could do it directly in a one-liner. My first idea was to use the LET operator in combination with CONV (Option 2). This works, but does not look very intuitive, and I noticed it can be done even simpler without using LET (Option 3). And if you already have a typed variable, you can do it even shorter with a single CONV (Option 4).
* Option 1
DATA(date_1) = cl_bs_period_toolset_basics=>get_last_day_prev_month( sy-datum ).
*Option 2
DATA(date_2) = CONV d( LET x = CONV d( sy-datum(6) && '01' ) IN x - 1 ).
*Option 3
DATA(date_3) = CONV d( CONV d( sy-datum(6) && '01' ) - 1 ).
* Option 4
DATA date_4 TYPE datum.
date_4 = CONV d( sy-datum(6) && '01' ) - 1.
cl_demo_output=>write_data( date_1 ).
cl_demo_output=>write_data( date_2 ).
cl_demo_output=>write_data( date_3 ).
cl_demo_output=>write_data( date_4 ).
cl_demo_output=>display( ).
All in all, I have to say that using the get_last_day_prev_month method is still the best solution as it is much more readable.
[SAPUI5] Extension vs Adaption Project
I was wondering for quite some time, what the difference is between Extension Projects and Adaptions Projects. In the comments to this blog post, I finally found the answer from Oliver Graeff:
Adaptation projects are one of the capabilities of SAPUI5 flexibility, which lets developers, key users and end users adapt/extend SAPUI5 applications. Adaptation projects are the go-to solution for developer adaptation in SAPUI5 and are the ‘next-generation’ extension projects. Using the concepts of SAPUI5 flexibility, adaptation projects offer many more possibilities, such as extending SAP Fiori elements applications or extending apps without pre-defined extension points.
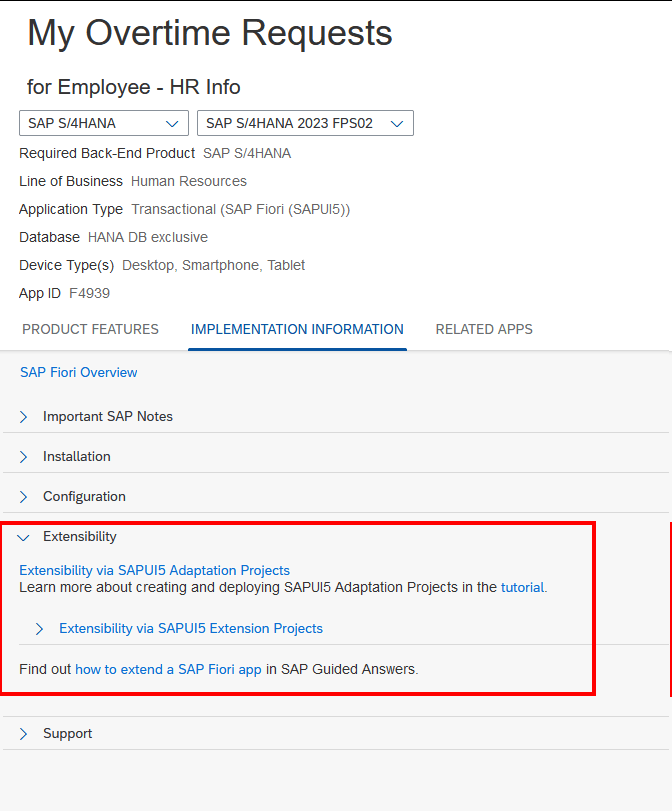
To check for a specific application, what the recommended extension approach is, simply go to the Fiori Reference Library, search for your app, choose the backend system (S/4 or Business Suite) and the current release version, navigate to Implementation Information and expand Extensibility. For example, My Overtime Requests on S/4HANA can be extended via an Adaption Project.
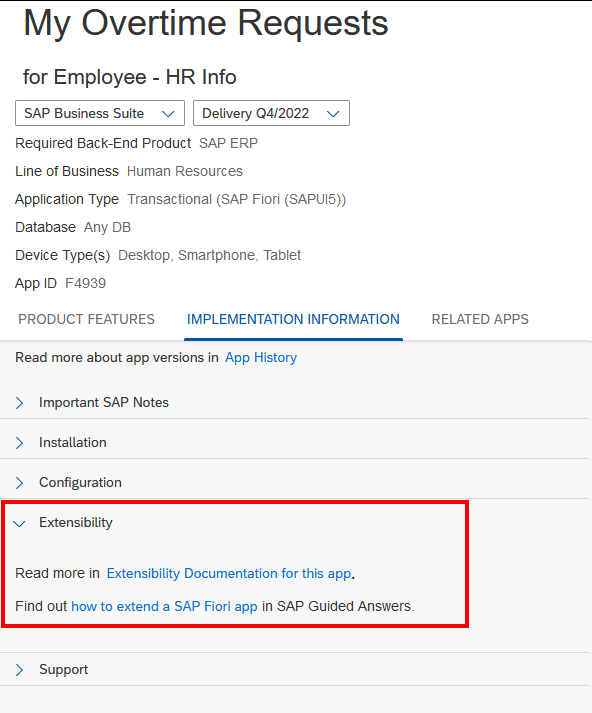
But on R/3, the only approach is an Extension Project.
Further helpful links:
Extending an SAP Fiori Application for an On-Premise System
Working with an Adaptation Project
Working with an SAPUI5 Extension Project
https://ga.support.sap.com/dtp/viewer/#/tree/1910/actions/24709
https://developers.sap.com/group.sapui5-adaptation-projects.html
https://sapui5.hana.ondemand.com/#/topic/a269671fc49e4c75920c108961bf31f2
[Homelab] Notes on “How To Run A Server At Home Without An IPv4 Address”
Since my domain provider does not support DynDNS, I can only create subdomains for my VPS with a static IP address, but not for any of my services hosted at home. Fortunately, there is a really cool workaround I’ve been using for some years, which I got from here: https://blog.wirelessmoves.com/2019/06/how-to-run-a-server-at-home-without-an-ipv4-address.html
Now with the migration to a new server running Ubuntu 24.04, I had to redo the steps and noticed three minor differences.
# The .ssh folder and authorized_keys file did not exist per default
mkdir .ssh
sudo nano .ssh/authorized_keys
# The systemd command to restart the ssh service
sudo systemctl restart ssh.service
# Insted of netstat I had to use 'ss' to monitor the tcp ports
watch -n 0.5 "ss -tulpn"
Since I’m really not a Linux or command line expert and would surely forget about it otherwise, I’m writing it down for my next server migration 🙂
[NAS] IPMI Docker
In my TrueNAS Server I use an ASRock Rack C2550D4I motherboard, which is quite old. It has a Java IPMI Interface, which was/is really handy. The problem is that it requires an old version of Java, and I haven’t had a computer in the household with Java installed at all for a few years, let alone a version that old. But luckily I recently stumbled across this docker project: https://github.com/solarkennedy/ipmi-kvm-docker
The setup is super easy and with the help of this cool project, I can finally use the IPMI functionality of my NAS again.
version: '3.9'
services:
ipmi-kvm-docker:
image: solarkennedy/ipmi-kvm-docker
environment:
- RES=1600x900x24
ports:
- '8080:8080'
[Home Assistant] Person card with step counter
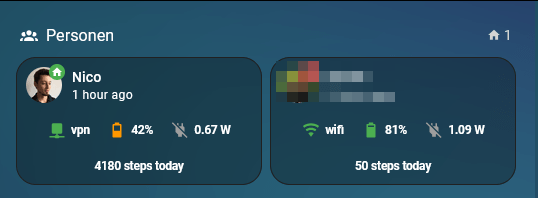
I recently enhanced the person cards on my dashboard to display some mobile phone sensor data (check here). In addition, I now also added the daily steps by using the Steps sensor of my mobile phone in combination with a utility helper sensor, which counts the daily steps, as the mobile Steps sensor is an increasing counter without daily reset. This is how it looks now:
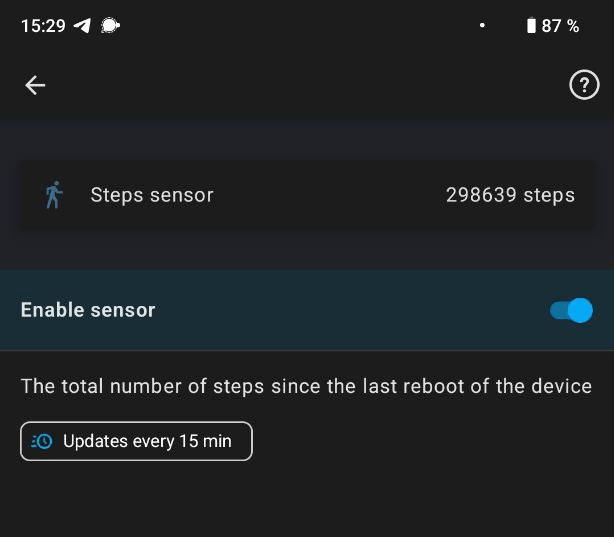
To include the daily steps, you first have to enable the Steps sensor in the Home Assistant Companion App on your mobile phone.
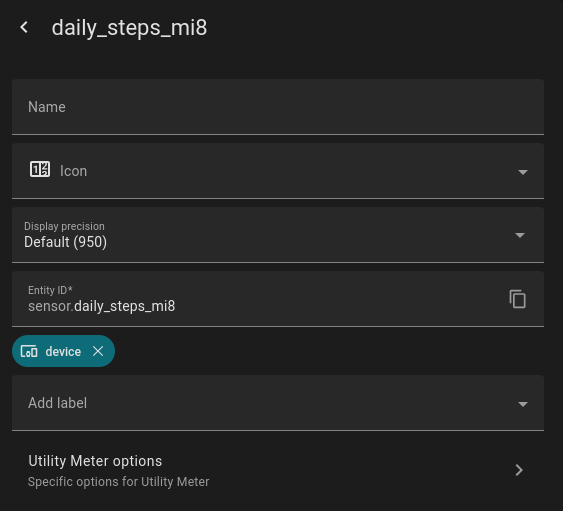
Next, create a utility sensor which uses the Steps sensor as Input and daily resets the counted steps.
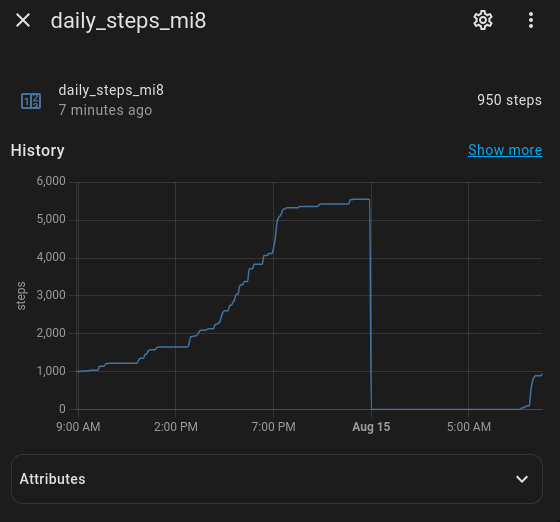
The utility sensor history should look like this after a few days:
Now we can add the utility sensor to the dashboard. As I’m using the vertical-stack-in-card, I simply had to add a new horizontal-stack to the person card to get a new line, and include a mushroom-chips-card which displays the steps.
- type: horizontal-stack
cards:
- type: custom:mushroom-chips-card
alignment: center
card_mod:
style: |
ha-card {
--chip-font-size: 0.32em;
--chip-icon-size: 0.5em;
--chip-border-width: 0;
--chip-box-shadow: none;
--chip-background: none;
--chip-border: none;
--chip-spacing: none;
--chip-font-weight: bold;
}
chips:
- type: template
entity: sensor.daily_steps_mi8
content: "{{ states('sensor.daily_steps_mi8')}} steps today"
tap_action:
action: more-info
I noticed, that the Steps sensor sometimes does not count steps, and it helps to have some separate steps counter app running on the phone like Paseo.
